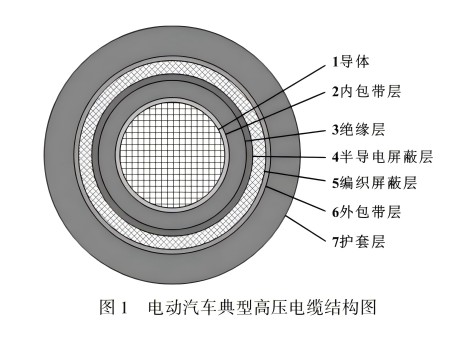
The new era of new energy automobile industry shoulders the dual mission of industrial transformation and upgrading and protection of the atmospheric environment, which greatly drives the industrial development of high-voltage cables and other related accessories for electric vehicles, and cable manufacturers and certification bodies have invested a lot of energy into the research and development of high-voltage cables for electric vehicles. High voltage cables for electric vehicles have high performance requirements in all aspects, and should meet the RoHSb standard, flame retardant grade UL94V-0 standard requirements and soft performance. This paper introduces the materials and preparation technology of high voltage cables for electric vehicles.
1.The material of high voltage cable
(1) Conductor material of the cable
At present, there are two main materials of cable conductor layer: copper and aluminum. A few companies think that aluminum core can greatly reduce their production costs, by adding copper, iron, magnesium, silicon and other elements on the basis of pure aluminum materials, through special processes such as synthesis and annealing treatment, improve the electrical conductivity, bending performance and corrosion resistance of the cable, in order to meet the requirements of the same load capacity, to achieve the same effect as copper core conductors or even better. Thus, the production cost is greatly saved. However, most enterprises still regard copper as the main material of the conductor layer, first of all, the resistivity of copper is low, and then most of the performance of copper is better than that of aluminum at the same level, such as large current carrying capacity, low voltage loss, low energy consumption and strong reliability. At present, the selection of conductors generally uses the national standard 6 soft conductors (single copper wire elongation must be greater than 25%, the diameter of the monofilament is less than 0.30) to ensure the softness and toughness of the copper monofilament. Table 1 lists the standards that must be met for commonly used copper conductor materials.
(2) Insulating layer materials of cables
The internal environment of electric vehicles is complex, in the selection of insulating materials, on the one hand, to ensure the safe use of insulation layer, on the other hand, as far as possible to choose easy processing and widely used materials. At present, the commonly used insulating materials are polyvinyl chloride (PVC), cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), silicone rubber, thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), etc., and their main properties are shown in Table 2.
Among them, PVC contains lead, but the RoHS Directive prohibits the use of lead, mercury, cadmium, hexvalent chromium, polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE) and polybrominated biphenyls (PBB) and other harmful substances, so in recent years PVC has been replaced by XLPE, silicone rubber, TPE and other environmentally friendly materials.
(3) Cable shielding layer material
The shielding layer is divided into two parts: semi-conductive shielding layer and braided shielding layer. The volume resistivity of the semi-conductive shielding material at 20 ° C and 90 ° C and after aging is an important technical index to measure the shielding material, which indirectly determines the service life of the high-voltage cable. Common semi-conductive shielding materials include ethylene-propylene rubber (EPR), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polyethylene (PE) based materials. In the case that the raw material has no advantage and the quality level cannot be improved in the short term, scientific research institutions and cable material manufacturers focus on the research of the processing technology and formula ratio of the shielding material, and seek innovation in the composition ratio of the shielding material to improve the overall performance of the cable.
2.High voltage cable preparation process
(1) Conductor strand technology
The basic process of cable has been developed for a long time, so there are also their own standard specifications in the industry and enterprises. In the process of wire drawing, according to the untwisting mode of single wire, the stranding equipment can be divided into untwisting stranding machine, untwisting stranding machine and untwisting/untwisting stranding machine. Due to the high crystallization temperature of copper conductor, the annealing temperature and time are longer, it is appropriate to use the untwisting stranding machine equipment to carry out continuous pulling and continuous pulling monwire to improve the elongation and fracture rate of wire drawing. At present, the cross-linked polyethylene cable (XLPE) has completely replaced the oil paper cable between 1 and 500kV voltage levels. There are two common conductor forming processes for XLPE conductors: circular compaction and wire twisting. On the one hand, the wire core can avoid the high temperature and high pressure in the cross-linked pipeline to press its shielding material and insulation material into the stranded wire gap and cause waste; On the other hand, it can also prevent water infiltration along the conductor direction to ensure the safe operation of the cable. The copper conductor itself is a concentric stranding structure, which is mostly produced by ordinary frame stranding machine, fork stranding machine, etc. Compared with the circular compaction process, it can ensure the conductor stranding round formation.
(2) XLPE cable insulation production process
For the production of high voltage XLPE cable, catenary dry cross-linking (CCV) and vertical dry cross-linking (VCV) are two forming processes.
(3) Extrusion process
Earlier, cable manufacturers used a secondary extrusion process to produce cable insulation core, the first step at the same time extrusion conductor shield and insulation layer, and then cross-linked and wound to the cable tray, placed for a period of time and then extrusion insulation shield. During the 1970s, a 1+2 three-layer extrusion process appeared in the insulated wire core, allowing the internal and external shielding and insulation to be completed in a single process. The process first extrudes the conductor shield, after a short distance (2~5m), and then extrudes the insulation and insulation shield on the conductor shield at the same time. However, the first two methods have great drawbacks, so in the late 1990s, cable production equipment suppliers introduced a three-layer co-extrusion production process, which extruded conductor shielding, insulation and insulation shielding at the same time. A few years ago, foreign countries also launched a new extruder barrel head and curved mesh plate design, by balancing the screw head cavity flow pressure to alleviate the accumulation of material, extend the continuous production time, replacing the non-stop change of specifications of the head design can also greatly save downtime costs and improve efficiency.
3. Conclusion
New energy vehicles have good development prospects and a huge market, need a series of high voltage cable products with high load capacity, high temperature resistance, electromagnetic shielding effect, bending resistance, flexibility, long working life and other excellent performance into production and occupy the market. Electric vehicle high-voltage cable material and its preparation process have broad prospects for development. Electric vehicle can not improve production efficiency and ensure the use of safety without high-voltage cable.
Post time: Aug-23-2024