During the installation and use of the cable, it is damaged by mechanical stress, or the cable is used for a long time in a humid and watery environment, which will cause the external water to gradually penetrate into the cable. Under the action of electric field, the probability of generating water tree on the cable insulation surface will increase. The water tree formed by electrolysis will crack the insulation, reduce the overall insulation performance of the cable, and affect the service life of the cable. Therefore, the use of waterproof cables is crucial.
Cable waterproof mainly considers water seepage along the direction of the cable conductor and along the radial direction of the cable through the cable sheath. Therefore, the radial waterproof and longitudinal water-blocking structure of the cable can be used.
1.Cable radial waterproof
The main purpose of radial waterproofing is to prevent the surrounding external water flow into the cable during use. Waterproof structure has the following options.
1.1 Polyethylene sheath waterproof
Polyethylene sheath waterproof is only applicable to the general requirements of waterproof. For cables immersed in water for a long time, the waterproof performance of polyethylene sheathed waterproof power cables needs to be improved.
1.2 Metal sheath waterproof
The radial waterproof structure of low-voltage cables with rated voltage of 0.6kV/1kV and above is generally realized through the outer protective layer and the internal longitudinal wrapping of double-sided aluminum-plastic composite belt. Medium voltage cables with rated voltage 3.6kV/6kV and above are radial waterproof under the joint action of aluminum-plastic composite belt and semi-conductive resistance hose. High voltage cables with higher voltage levels can be waterproof with metal sheaths such as lead sheaths or corrugated aluminum sheaths.
Comprehensive sheath waterproof is mainly applicable to cable trench, directly buried underground water and other places.
2. Cable vertically waterproof
Longitudinal water resistance can be considered to make the cable conductor and insulation have a water resistance effect. When the outer protective layer of the cable is damaged due to external forces, the surrounding moisture or moisture will penetrate vertically along the cable conductor and insulation direction. In order to avoid moisture or moisture damage to the cable, we can use the following methods to protect the cable.
(1)Water blocking tape
A water-resisting expansion zone is added between the insulated wire core and the aluminum-plastic composite strip. The Water blocking tape is wrapped around the insulated wire core or the cable core, and the wrapping and covering rate is 25%. The Water blocking tape expands when it encounters water, which increases the tightness between the Water blocking tape and the cable sheath, so as to achieve the water-blocking effect.
(2)Semi-conductive water blocking tape
Semi-conductive water blocking tape is widely used in medium voltage cable, by wrapping the Semi-conductive water blocking tape around the metal shielding layer, to achieve the purpose of longitudinal water resistance of the cable. Although the water blocking effect of the cable is improved, the outer diameter of the cable increases after the cable is wrapped around the water blocking tape.
(3)Water blocking filling
Water-blocking filling materials are usually water-blocking yarn (rope) and water-blocking powder. The water-blocking powder is mostly used to block water between the twisted conductor cores. When the water-blocking powder is difficult to attach to the conductor monofilament, the positive water adhesive can be applied outside the conductor monofilament, and the water-blocking powder can be wrapped outside the conductor. Water-blocking yarn (rope) is often used to fill the gaps between medium-pressure three-core cables.
3 General structure of cable water resistance
According to the different use environment and requirements, the cable water resistance structure includes radial waterproof structure, longitudinal (including radial) water resistance structure and all-round water resistance structure. The water-blocking structure of a three-core medium voltage cable is taken as an example.
3.1 Radial waterproof structure of three-core medium voltage cable
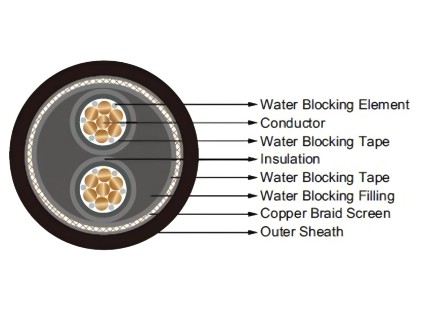
Radial waterproofing of three-core medium voltage cable generally adopts Semi-conductive water blocking tape and double-sided plastic coated aluminum tape to achieve water resistance function. Its general structure is: conductor, conductor shielding layer, insulation, insulation shielding layer, metal shielding layer (copper tape or copper wire), ordinary filling, semi-conductive water blocking tape, double-sided plastic coated aluminum tape longitudinal package, outer sheath.
3.2 Three-core medium voltage cable longitudinal water resistance structure
The three-core medium voltage cable also uses semi-conductive water blocking tape and double-sided plastic coated aluminum tape to achieve water resistance function. In addition, the water blocking rope is used to fill the gap between the three core cables. Its general structure is: conductor, conductor shielding layer, insulation, insulation shielding layer, semi-conductive water blocking tape, metal shielding layer (copper tape or copper wire), water blocking rope filling, semi-conductive water blocking tape, outer sheath.
3.3 Three-core medium voltage cable all-round water resistance structure
The cable’s all-round water blocking structure requires that the conductor also has a water blocking effect, and combined with the requirements of radial waterproof and longitudinal water blocking, to achieve all-round water blocking. Its general structure is: water-blocking conductor, conductor shielding layer, insulation, insulation shielding layer, semi-conductive water blocking tape, metal shielding layer (copper tape or copper wire), water-blocking rope filling, semi-conductive water blocking tape, double-sided plastic coated aluminum tape longitudinal package, outer sheath.
The three-core water-blocking cable can be improved to three single-core water-blocking cable structures (similar to the three-core aerial insulated cable structure). That is, each cable core is first produced according to the single-core water-blocking cable structure, and then three separate cables are twisted through the cable to replace the three-core water-blocking cable. In this way, not only improve the water resistance of the cable, but also provide convenience for the cable processing and later installation and laying.
4.Precautions for making water-blocking cable connectors
(1) Select the appropriate joint material according to the specifications and models of the cable to ensure the quality of the cable joint.
(2) Do not choose rainy days when making water-blocking cable joints. This is because the cable water will seriously affect the service life of the cable, and even short circuit accidents will occur in serious cases.
(3) Before making water-resistant cable joints, carefully read the manufacturer’s product instructions.
(4) When pressing the copper pipe at the joint, it can not be too hard, as long as it is pressed to the position. The copper end face after crimping should be filed flat without any burrs.
(5) When using a blowtorch to make a cable heat shrink joint, pay attention to the blowtorch moving back and forth, not only in one direction constantly blowtorch.
(6) The size of the cold shrink cable joint must be done in strict accordance with the drawing instructions, especially when extracting the support in the reserved pipe, it must be careful.
(7) If necessary, sealant can be used at the cable joints to seal and further improve the waterproof ability of the cable.
Post time: Aug-28-2024