With the advancement of digital transformation and societal intelligence, the use of optical cables is becoming ubiquitous. Optical fibers, as the medium for information transmission in optical cables, offer high bandwidth, high speed, and low latency transmission. However, with a diameter of only 125μm and being made of glass fibers, they are fragile. Therefore, to ensure the safe and reliable transmission of optical fibers across diverse environments such as sea, land, air, and space, high-quality fiber materials are needed as reinforcement components.
Aramid fiber is a high-tech synthetic fiber that has evolved since its industrialization in the 1960s. With several iterations, it has resulted in multiple series and specifications. Its unique properties—light weight, flexibility, high tensile strength, high tensile modulus, low coefficient of linear expansion, and excellent environmental resistance—make it an ideal reinforcement material for optical cables.
1. Composition material of Optical Cables
Optical cables consist of the strengthened core, cable core, sheath, and outer protective layer. The core structure can be single-core (solid and tube bundle types) or multi-core (flat and unitized types). The outer protective layer can be metallic or non-metallic armored.
2. Composition of Aramid Fiber in Optical Cables
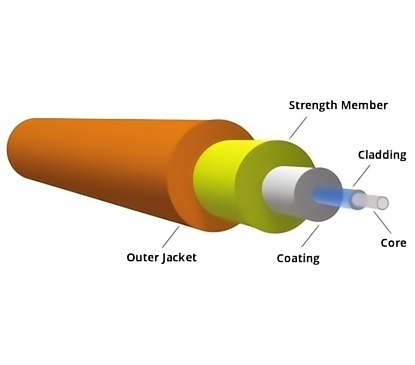
From the inside to the outside, the optical cable includes the optical fiber, loose tube, insulation layer, and sheath. The loose tube surrounds the optical fiber, and the space between the optical fiber and loose tube is filled with gel. The insulation layer is made of aramid, and the outer sheath is a low-smoke, halogen-free flame-retardant polyethylene sheath, covering the aramid layer.
3. Application of Aramid Fiber in Optical Cables
(1) Indoor Optical Cables
Single- and double-core soft optical cables are characterized by high bandwidth, high speed, and low loss. They are widely used in data centers, server rooms, and fiber-to-the-desk applications. In densely deployed mobile broadband networks, large numbers of base stations and indoor dense time-division systems require the use of long-distance optical cables and micro-optical hybrid cables. Whether it is single- or double-core soft optical cables or long-distance optical cables and micro-optical hybrid cables, the use of high-strength, high-modulus, flexible aramid fiber as a reinforcement material ensures mechanical protection, flame retardancy, environmental resistance, and compliance with cable requirements.
(2)All-Dielectric Self-Supporting (ADSS) Optical Cable
With rapid development in China’s power energy infrastructure and ultra-high-voltage projects, the deep integration of power communication networks with 5G technology is essential for smart grid construction. ADSS optical cables are used along power lines, requiring them to perform well in high electromagnetic field environments, reduce the cable’s weight to minimize load on power poles, and achieve an all-dielectric design to prevent lightning strikes and ensure safety. High-strength, high-modulus, low-coefficient-of-expansion aramid fibers effectively protect the optical fibers in ADSS cables.
(3)Tethered Optoelectronic Composite Cables
Tethered cables are key components that connect control platforms and controlled equipment such as balloons, airships, or drones. In the era of rapid information, digitalization, and intelligence, optoelectronic composite tether cables need to provide both electrical power and high-speed information transmission for system equipment.
(4)Mobile Optical Cables
Mobile optical cables are mainly used in temporary networking scenarios, such as oil fields, mines, ports, live television broadcasts, communication line repairs, emergency communication, earthquake resistance, and disaster relief. These cables require light weight, small diameter, and portability, along with flexibility, wear resistance, oil resistance, and low-temperature resistance. The use of flexible, high-strength, high-modulus aramid fibers as reinforcement ensures the stability, pressure resistance, wear resistance, oil resistance, low-temperature flexibility, and flame retardancy of mobile optical cables.
(5)Guided Optical Cables
Optical fibers are ideal for high-speed transmission, wide bandwidth, strong electromagnetic interference resistance, low loss, and long transmission distances. These characteristics make them widely used in wired guidance systems. For missile guidance cables, aramid fibers protect the fragile optical fibers, ensuring high-speed deployment even during missile flight.
(6)Aerospace High-Temperature Installation Cables
Due to their excellent properties such as high strength, high modulus, low density, flame retardancy, high-temperature resistance, and flexibility, aramid fibers are extensively used in aerospace cables. By plating aramid fibers with metals like zinc, silver, aluminum, nickel, or copper, conductive aramid fibers are created, offering electrostatic protection and electromagnetic shielding. These fibers can be used in aerospace cables as shielding elements or signal transmission components. Additionally, conductive aramid fibers can significantly reduce weight while enhancing performance, supporting the development of microwave communication, RF cables, and other aerospace defense projects. These fibers also offer electromagnetic shielding for high-frequency flexing areas in aircraft landing gear cables, spacecraft cables, and robotics cables.
Post time: Nov-11-2024