In the field of New Energy Vehicles (EV, PHEV, HEV), the choice of materials for high voltage cables is crucial to the vehicle’s safety, durability, and performance. Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) and silicone rubber are two of the most common insulation materials, but they have significant differences in high-temperature performance, insulation properties, mechanical strength, and more.
Overall, both XLPE and silicone rubber are widely used in automotive interior cables. So, which material is better suited for high voltage cables in new energy vehicles?
Why do High Voltage Cables for New Energy Vehicles Require High-Performance Insulation Materials?
High voltage cables in new energy vehicles are mainly used for the battery pack, motor, electronic control system, and charging system, with operating voltages ranging from 600V to 1500V, or even higher.
This requires the cables to have:
1) Excellent insulation performance to prevent electrical breakdown and ensure safety.
2) Outstanding high-temperature resistance to withstand harsh operating environments and prevent insulation degradation.
3) Strong resistance to mechanical stresses, bending, vibration, and wear.
4) Good chemical corrosion resistance to adapt to complex environments and extend service life.
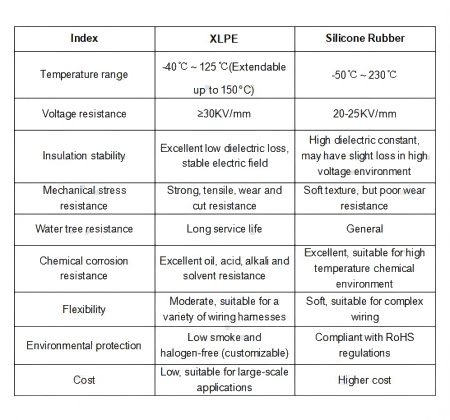
Currently, the insulation layers of high voltage cables in new energy vehicles primarily use XLPE or silicone rubber. Below, we will make a detailed comparison of these two materials.
From the table, it can be seen that XLPE performs better in terms of voltage resistance, mechanical strength, aging resistance, and cost control, while silicone rubber has advantages in high-temperature resistance and flexibility.
Why is XLPE the Preferred Material for High Voltage Cables in New Energy Vehicles?
1) Stronger Insulation Performance: XLPE has a higher dielectric strength (≥30kV/mm), which makes it better at resisting electrical breakdown risks in high voltage environments compared to silicone rubber. Additionally, XLPE has a low dielectric loss, ensuring stable long-term performance, making it suitable for new energy vehicle power systems.
2) Better Mechanical Properties: During driving, vibrations from the vehicle body can impose mechanical stress on the cables. XLPE has higher tensile strength, better wear resistance, and superior cut resistance, making it more suitable for long-term use and reducing maintenance costs compared to silicone rubber.
3) Better Aging Resistance: XLPE has excellent resistance to water tree aging, ensuring the cable remains stable in high humidity and high electric field environments. This is crucial for new energy vehicles, especially in high-load applications such as high-voltage battery packs and fast-charging systems.
4) Moderate Flexibility to Meet Wiring Requirements: Compared to silicone rubber, XLPE offers moderate flexibility, balancing wiring flexibility and mechanical strength. It performs excellently in applications such as in-vehicle high-voltage harnesses, motor control lines, and battery pack connections.
5) More Cost-Effective: XLPE is more cost-effective than silicone rubber, supporting mass production. It has become the mainstream material for high voltage cables in new energy vehicles.
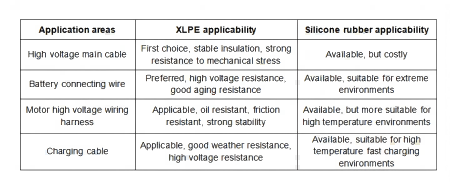
Application Scenario Analysis: XLPE vs Silicone Rubber
XLPE, with its excellent voltage resistance, mechanical strength, and cost advantages, is more competitive in the application of high-voltage cables for new energy vehicles.
As new energy vehicle technology continues to advance, XLPE materials are also being upgraded to meet higher demands in application scenarios:
1) High-Temperature Resistant XLPE (150℃-200℃): Suitable for the next-generation high-efficiency electric drive systems.
2) Low-Smoke Zero-Halogen Cross-linked Polyethylene (LSZH): Complies with environmental standards for new energy vehicles.
3) Optimized Shielding Layer: Enhances resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improves the overall electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) of the vehicle.
Overall, XLPE occupies a dominant position in the high-voltage cable sector for new energy vehicles due to its excellent insulation performance, voltage resistance, mechanical strength, and cost advantages. While silicone rubber is suitable for extreme high-temperature environments, its higher cost makes it suitable for special needs. For mainstream high-voltage cables in new energy vehicles, XLPE is the best choice and can be widely applied in key areas such as battery harnesses, high-voltage motor cables, and fast-charging cables.
In the context of the rapid development of the new energy vehicle industry, companies should consider factors such as application scenarios, temperature resistance requirements, and cost budgets when selecting high-voltage cable materials to ensure the safety and durability of the cables.
Post time: Feb-28-2025