Marine optical fiber cables are specifically designed for ocean environments, providing stable and reliable data transmission. They are not only used for internal ship communication but also widely applied in transoceanic communication and data transmission for offshore oil and gas platforms, playing a crucial role in modern marine communication systems. To ensure the stability of offshore operations, marine optical fiber cables are designed to be waterproof, pressure-resistant, corrosion-resistant, mechanically robust, and highly flexible.
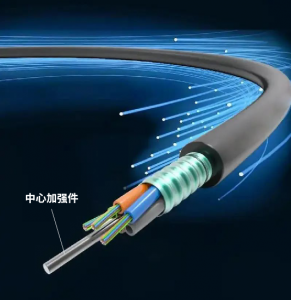
Generally, the structure of marine optical fiber cables includes at least a fiber unit, sheath, armor layer, and outer jacket. For special designs or applications, marine optical fiber cables may omit the armor layer and instead use more wear-resistant materials or special outer jackets. Additionally, to adapt to different environments, marine optical fiber cables may also include fire-resistant layers, central/reinforcing members, and additional water-blocking elements.
(1) Optical Fiber Unit
The fiber unit is the core component of marine optical fiber cables, containing one or more optical fibers.
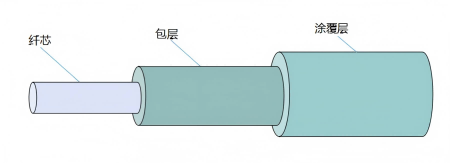
Optical fibers are the core part of the cable, typically consisting of a core, cladding, and coating, with a concentric circular structure. The core, made of high-purity silica, is responsible for transmitting optical signals. The cladding, also made of high-purity silica, surrounds the core, providing a reflective surface and optical isolation, as well as mechanical protection. The coating, the outermost layer of the fiber, is made of materials such as acrylate, silicone rubber, and nylon, protecting the fiber from moisture and mechanical damage.
Optical fibers are generally classified into single-mode fibers (e.g., G.655, G652D) and multi-mode fibers (e.g., OM1-OM4), with different transmission performance characteristics. Key transmission properties include maximum attenuation, minimum bandwidth, effective refractive index, numerical aperture, and maximum dispersion coefficient, which determine the efficiency and distance of signal transmission.
The fibers are surrounded by loose or tight buffer tubes to reduce interference between fibers and external environmental impacts. The design of the fiber unit ensures efficient data transmission, making it the most fundamental and critical part of marine optical fiber cables.
(2) Sheath
The fiber sheath is a key component of the cable, protecting the optical fibers. Based on structure, it can be divided into tight buffer tubes and loose buffer tubes.
Tight buffer tubes are typically made of materials such as polypropylene resin (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and halogen-free flame-retardant polyethylene (HFFR PE). Tight buffer tubes adhere closely to the fiber surface, leaving no significant gaps, which minimizes fiber movement. This tight coverage provides direct protection for the fibers, preventing moisture ingress and offering high mechanical strength and resistance to external interference.
Loose buffer tubes are usually made of high-modulus PBT plastic, filled with water-blocking gel to provide cushioning and protection. Loose buffer tubes offer excellent flexibility and lateral pressure resistance. The water-blocking gel allows the fibers to move freely within the tube, facilitating fiber extraction and maintenance. It also provides additional protection against damage and moisture ingress, ensuring the stability and safety of the cable in humid or underwater environments.
(3) Armor Layer
The armor layer is located inside the outer jacket and provides additional mechanical protection, preventing physical damage to the marine optical fiber cable. The armor layer is typically made of galvanized steel wire braid (GSWB). The braided structure covers the cable with galvanized steel wires, usually with a coverage rate of no less than 80%. The armor structure offers extremely high mechanical protection and tensile strength, while the braided design ensures flexibility and a smaller bending radius (the dynamic allowable bending radius for marine optical fiber cables is 20D). This makes it suitable for applications requiring frequent movement or bending. Additionally, the galvanized steel material provides extra corrosion resistance, making it ideal for use in humid or salt-spray environments.
(4) Outer Jacket
The outer jacket is the direct protective layer of marine optical fiber cables, designed to withstand sunlight, rain, seawater erosion, biological damage, physical impact, and UV radiation. The outer jacket is typically made of environmentally resistant materials such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and low-smoke zero-halogen (LSZH) polyolefin, offering excellent UV resistance, weather resistance, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy. This ensures the cable remains stable and reliable under harsh marine conditions. For safety reasons, most marine optical fiber cables now use LSZH materials, such as LSZH-SHF1, LSZH-SHF2, and LSZH-SHF2 MUD. LSZH materials produce very low smoke density and contain no halogens (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, etc.), avoiding the release of toxic gases during combustion. Among these, LSZH-SHF1 is the most commonly used.
(5) Fire-Resistant Layer
In critical areas, to ensure the continuity and reliability of communication systems (e.g., for fire alarms, lighting, and communication during emergencies), some marine optical fiber cables include a fire-resistant layer. Loose buffer tube cables often require the addition of mica tape to enhance fire resistance. Fire-resistant cables can maintain communication capabilities for a certain period during a fire, which is crucial for ship safety.
(6) Reinforcing Members
To enhance the mechanical strength of marine optical fiber cables, central reinforcing members such as phosphated steel wires or fiber-reinforced plastic (FRP) are added. These increase the cable’s strength and tensile resistance, ensuring stability during installation and use. Additionally, auxiliary reinforcing members such as aramid yarn can be added to improve the cable’s strength and chemical corrosion resistance.
(7) Structural Improvements
With technological advancements, the structure and materials of marine optical fiber cables are continuously evolving. For example, all-dry loose tube cables eliminate traditional water-blocking gel and use dry water-blocking materials in both the loose tubes and cable core, offering environmental benefits, lighter weight, and gel-free advantages. Another example is the use of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer (TPU) as the outer jacket material, which provides a wider temperature range, oil resistance, acid resistance, alkali resistance, lighter weight, and smaller space requirements. These innovations demonstrate the ongoing improvements in marine optical fiber cable design.
(8) Summary
The structural design of marine optical fiber cables takes into account the special requirements of ocean environments, including waterproofing, pressure resistance, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. The high performance and reliability of marine optical fiber cables make them an indispensable component of modern marine communication systems. As marine technology advances, the structure and materials of marine optical fiber cables continue to evolve to meet the demands of deeper ocean exploration and more complex communication needs.
About ONE WORLD (OW Cable)
ONE WORLD (OW Cable) is a leading global supplier of high-quality raw materials for the wire and cable industry. Our product portfolio includes fiber-reinforced plastic (FRP), low-smoke zero-halogen (LSZH) materials, halogen-free flame-retardant polyethylene (HFFR PE), and other advanced materials designed to meet the stringent requirements of modern cable applications. With a commitment to innovation, quality, and sustainability, ONE WORLD (OW Cable) has become a trusted partner for cable manufacturers worldwide. Whether for marine optical fiber cables, power cables, communication cables, or other specialized applications, we provide the raw materials and expertise needed to ensure superior performance and reliability.
Post time: Mar-14-2025