High voltage cables and low voltage cables have distinct structural variances, impacting their performance and applications. The internal composition of these cables reveals the key disparities:
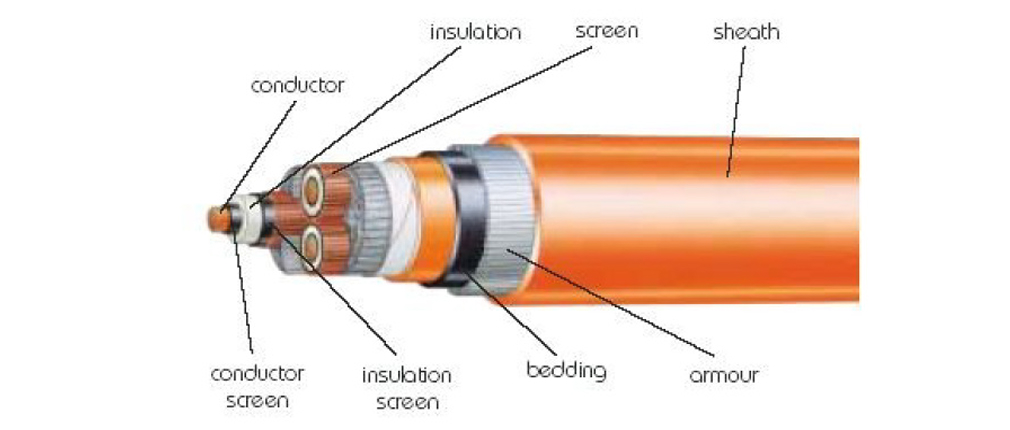
High Voltage Cable Structure:
1. Conductor
2. Inner Semiconducting Layer
3. Insulation Layer
4. Outer Semiconducting Layer
5. Metal Armor
6. Sheath Layer
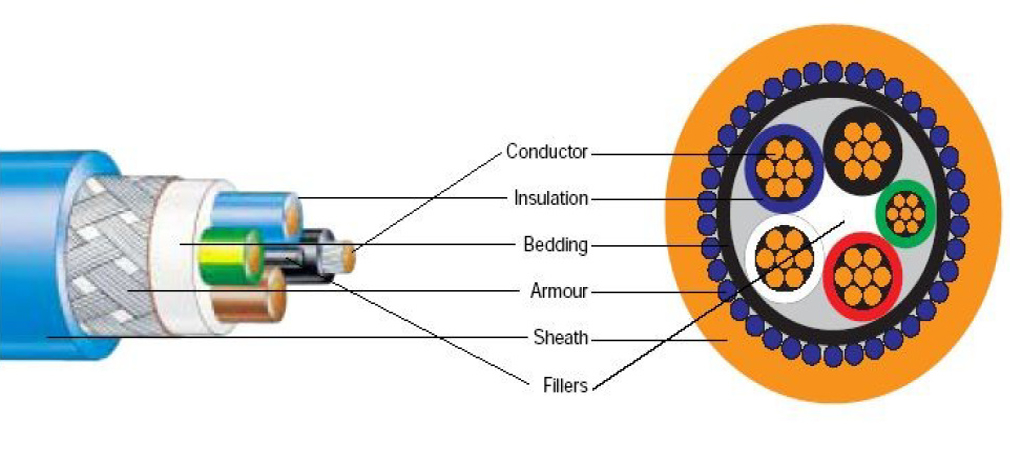
Low Voltage Cable Structure:
1. Conductor
2. Insulation Layer
3. Steel Tape (Not present in many low voltage cables)
4. Sheath Layer
The primary dissimilarity between high voltage and low voltage cables lies in the presence of a semiconducting layer and a shielding layer in high voltage cables. Consequently, high voltage cables tend to have significantly thicker insulation layers, resulting in a more complex structure and demanding manufacturing processes.
Semiconducting Layer:
The inner semiconducting layer functions to improve the electric field effect. In high voltage cables, the proximity between the conductor and insulation layer can create gaps, leading to partial discharges that damage the insulation. To mitigate this, a semiconducting layer acts as a transition between the metal conductor and insulation layer. Similarly, the outer semiconducting layer prevents localized discharges between the insulation layer and the metal sheath.
Shielding Layer:
The metal shielding layer in high voltage cables serves three main purposes:
1. Electric Field Shielding: Protects against external interference by shielding the electric field generated within the high voltage cable.
2. Conduction of Capacitive Current during Operation: Acts as a pathway for capacitive current flow during cable operation.
3. Short Circuit Current Pathway: In the event of insulation failure, the shielding layer provides a route for leakage current to flow to the ground, enhancing safety.
Distinguishing Between High Voltage and Low Voltage Cables:
1. Structural Examination: High voltage cables have more layers, evident upon peeling back the outermost layer to reveal metal armor, shielding, insulation, and the conductor. In contrast, low voltage cables typically expose insulation or conductors upon removal of the outer layer.
2. Insulation Thickness: High voltage cable insulation is notably thicker, generally exceeding 5 millimeters, while low voltage cable insulation is typically within 3 millimeters.
3. Cable Markings: The outermost layer of the cable often contains markings specifying cable type, cross-sectional area, rated voltage, length, and other relevant parameters.
Understanding these structural and functional disparities is crucial for selecting the appropriate cable for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Post time: Jan-27-2024

