A photoelectric composite cable is a new type of cable that combines optical fiber and copper wire, serving as a transmission line for both data and electrical power. It can address various issues related to broadband access, electrical power supply, and signal transmission. Let’s explore fiber-optic composite cables further:
1. Applications:
Photoelectric composite cables are suitable for a range of applications, including insulated communication optical cable projects, traffic communication optical cable projects, square optical cable projects, overhead optical cable installations, electrical power optical cable projects, and high-altitude optical cable installations.
2. Product Structure:
RVV: Consists of an inner conductor made of electric round copper wire, PVC insulation, a filler rope, and PVC sheathing.
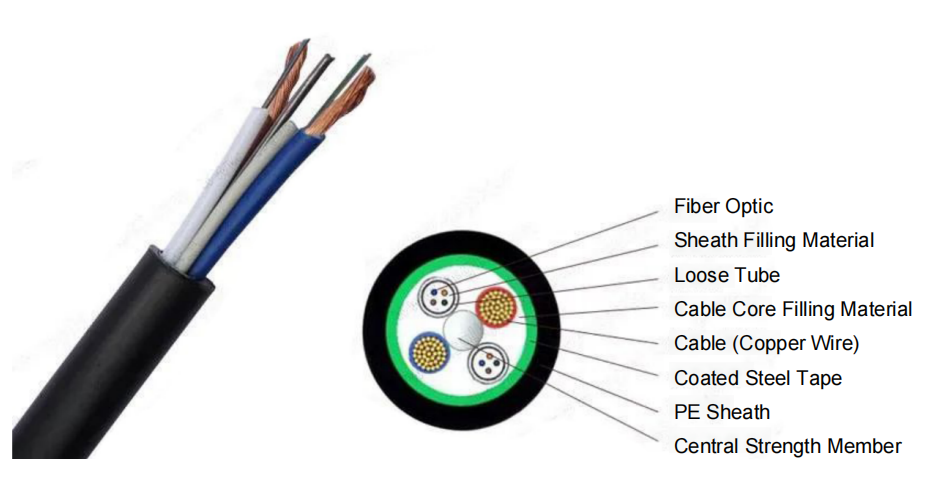
GYTS: Comprises a glass fiber conductor, a UV-cured coating, high-strength phosphated steel wire, coated steel tapes, and a polyethylene sheath.
3. Advantages:
1. Small outer diameter, lightweight, and minimal space requirements.
2. Low procurement costs for customers, reduced construction expenses, and cost-effective network development.
3. Excellent flexibility and resistance to lateral pressure, making installation easier.
4. Provides multiple transmission technologies, high adaptability to various equipment, strong scalability, and broad applicability.
5. Offers significant broadband access capabilities.
6. Cost savings by reserving optical fiber for future household connections, eliminating the need for secondary cabling.
7. Addresses power supply issues in network construction, avoiding the need for redundant power lines.
4. Mechanical Performance of Optical Cables:
Mechanical performance testing of optical cables includes various aspects such as tension, flattening, impact, repeated bending, twisting, coiling, and winding.
- All optical fibers within the cable should remain unbroken.
- The sheath should be free from visible cracks.
- The metal components within the optical cable should maintain electrical conductivity.
- No visible damage should occur to the cable core or its components within the sheath.
- Optical fibers should exhibit no additional residual attenuation after testing.
While photoelectric composite cables are designed with a PE outer sheath suitable for use in conduits containing water, it is essential to pay attention to waterproofing the cable ends during installation to prevent water ingress into the copper wire.
Post time: Oct-16-2023