Optical fiber is a slender, soft solid glass substance, which consists of three parts, fiber core, cladding, and coating, and can be used as a light transmission tool.
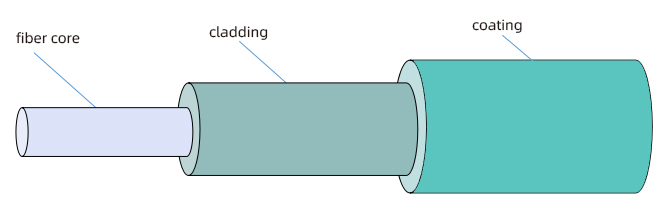
1.Fiber core: Located in the center of the fiber, the composition is high-purity silica or glass.
2.Cladding: Located around the core, its composition is also high-purity silica or glass. The cladding provides a reflective surface and light isolation for light transmission, and plays a certain role in mechanical protection.
3.Coating: The outermost layer of an optical fiber, consisting of acrylate, silicone rubber, and nylon. The coating protects the optical fiber from water vapor erosion and mechanical abrasion.
In maintenance, we often encounter situations where optical fibers are interrupted, and optical fiber fusion splicers can be used to re-splice the optical fibers.
The principle of the fusion splicer is that the fusion splicer must correctly find the cores of the optical fibers and align them accurately, and then melt the optical fibers through the high-voltage discharge arc between the electrodes and then push them forward for fusion.
For normal fiber splicing, the position of the splicing point should be smooth and tidy with low loss:
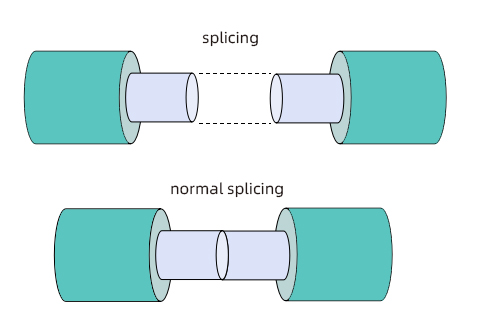
In addition, the following 4 situations will cause a large loss at the fiber splicing point, which needs to be paid attention to during splicing:
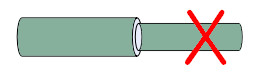
Inconsistent core size at both ends
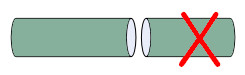
Air gap at both ends of the core
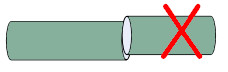
The center of the fiber core at both ends is not aligned
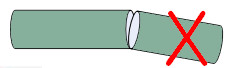
The fiber core angles at both ends are misaligned
Post time: Mar-13-2023

