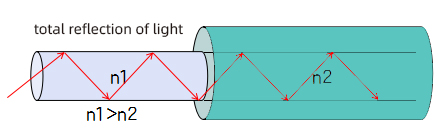
he realization of optical fiber communication is based on the principle of total reflection of light.
When light propagates into the center of the optical fiber, the refractive index n1 of the fiber core is higher than that of the cladding n2, and the loss of the core is lower than that of the cladding, so that the light will undergo total reflection, and its light energy is mainly transmitted in the core. Due to successive total reflections, light can be transmitted from one end to the other.
Classified by transmission mode: single-mode and multi-mode.
Single-mode has a small core diameter and can only transmit light waves of one mode.
Multi-mode optical fiber has a large core diameter and can transmit light waves in multiple modes.
We can also distinguish single-mode optical fiber from multi-mode optical fiber by the color of the appearance.
Most single-mode optical fibers have a yellow jacket and a blue connector, and the cable core is 9.0 μm. There are two central wavelengths of single-mode fiber: 1310 nm and 1550 nm. 1310 nm is generally used for short-distance, medium-distance or long-distance transmission, and 1550 nm is used for long-distance and ultra-long-distance transmission. The transmission distance depends on the transmission power of the optical module. The transmission distance of the 1310 nm single-mode port is 10 km, 30 km, 40 km, etc., and the transmission distance of the 1550 nm single-mode port is 40 km, 70 km, 100 km, etc.

Multi-mode optical fibers are mostly orange/gray jacket with black/beige connectors, 50.0 μm and 62.5 μm cores. The center wavelength of multi-mode fiber is generally 850 nm. The transmission distance of multi-mode fiber is relatively short, generally within 500 m.

Post time: Feb-17-2023

