Indoor optical cables are commonly used in structured cabling systems. Due to various factors such as building environment and installation conditions, the design of indoor optical cables has become more complex. The materials used for the optical fibers and cables are diverse, with mechanical and optical properties being emphasized differently. Common indoor optical cables include single-core branch cables, non-bundled cables, and bundled cables. Today, ONE WORLD will focus on one of the most common types of bundled optical cables: GJFJV.
GJFJV Indoor Optical Cable
1. Structural Composition
The industry-standard model for indoor optical cables is GJFJV.
GJ — Communication indoor optical cable
F — Non-metallic reinforcing component
J — Tight-buffered optical fiber structure
V — Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) sheath
Note: For sheath material naming, "H" stands for low smoke halogen-free sheath, and "U" stands for polyurethane sheath.
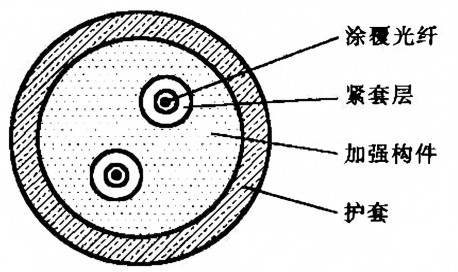
2. Indoor Optical Cable Cross-Section Diagram
Composition Materials and Features
1. Coated Optical Fiber (Composed of optical fiber and external coating layer)
The optical fiber is made of silica material, and the standard cladding diameter is 125 μm. The core diameter for single-mode (B1.3) is 8.6-9.5 μm, and for multi-mode (OM1 A1b) is 62.5 μm. The core diameter for multi-mode OM2 (A1a.1), OM3 (A1a.2), OM4 (A1a.3), and OM5 (A1a.4) is 50 μm.
During the drawing process of the glass optical fiber, a layer of elastic coating is applied using ultraviolet light to prevent contamination by dust. This coating is made of materials like acrylate, silicone rubber, and nylon.
The function of the coating is to protect the optical fiber surface from moisture, gas, and mechanical abrasion, and to enhance the microbend performance of the fiber, thereby reducing additional bending losses.
The coating can be colored during use, and the colors should conform to GB/T 6995.2 (Blue, Orange, Green, Brown, Gray, White, Red, Black, Yellow, Purple, Pink, or Cyan Green). It can also remain uncolored as natural.
2. Tight Buffer Layer
Materials: Environmentally friendly, flame-retardant polyvinyl chloride (PVC), low smoke halogen-free (LSZH) polyolefin, OFNR-rated flame-retardant cable, OFNP-rated flame-retardant cable.
Function: It further protects the optical fibers, ensuring their adaptability to various installation conditions. It offers resistance to tension, compression, and bending, and also provides water and moisture resistance.
Use: The tight buffer layer can be color-coded for identification, with color codes conforming to GB/T 6995.2 standards. For non-standard identification, color rings or dots may be used.
3. Reinforcing Components
Material: Aramid yarn, specifically poly(p-phenylene terephthalamide), a new type of high-tech synthetic fiber. It has excellent properties such as ultra-high strength, high modulus, high temperature resistance, acid and alkali resistance, lightweight, insulation, aging resistance, and long service life. At higher temperatures, it maintains stability, with a very low shrinkage rate, minimal creep, and high glass transition temperature. It also offers high corrosion resistance and non-conductivity, making it an ideal reinforcement material for optical cables.
Function: Aramid yarn is evenly spiraled around or placed longitudinally in the cable sheath to provide support, enhancing the cable’s tensile and pressure resistance, mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical stability.
These characteristics ensure the cable's transmission performance and service life. Aramid is also commonly used in the production of bulletproof vests and parachutes due to its excellent tensile strength.


4. Outer Sheath
Materials: Low smoke halogen-free flame-retardant polyolefin (LSZH), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or OFNR/OFNP-rated flame-retardant cables. Other sheath materials can be used as per customer requirements. Low smoke halogen-free polyolefin must meet the YD/T1113 standards; polyvinyl chloride should comply with GB/T8815-2008 for soft PVC materials; thermoplastic polyurethane should meet the YD/T3431-2018 standards for thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers.
Function: The outer sheath provides additional protection for the optical fibers, ensuring they can adapt to various installation environments. It also provides resistance to tension, compression, and bending, while offering water and moisture resistance. For high fire safety scenarios, low smoke halogen-free materials are used to improve cable safety, protecting personnel from harmful gases, smoke, and flames in the event of a fire.
Use: The sheath color should conform to GB/T 6995.2 standards. If the optical fiber is B1.3-type, the sheath should be yellow; for B6-type, the sheath should be yellow or green; for AIa.1-type, it should be orange; AIb-type should be gray; A1a.2-type should be cyan green; and A1a.3-type should be purple.
Application Scenarios
1. Commonly used in internal communication systems within buildings, such as offices, hospitals, schools, financial buildings, shopping malls, data centers, etc. It is mainly applied for interconnection between equipment in server rooms and communication connections with external operators. Additionally, indoor optical cables can be used in home network wiring, such as LANs and smart home systems.
2. Usage: Indoor optical cables are compact, lightweight, space-saving, and easy to install and maintain. Users can choose different types of indoor optical cables based on specific area requirements.
In typical homes or office spaces, standard indoor PVC cables can be used.
According to the national standard GB/T 51348-2019:
①. Public buildings with a height of 100m or more;
②. Public buildings with a height between 50m and 100m and an area exceeding 100,000㎡;
③. Data centers of B grade or above;
These should use flame-retardant optical cables with a fire rating no lower than low-smoke, halogen-free B1 grade.
In the UL1651 standard in the U.S., the highest flame-retardant cable type is OFNP-rated optical cable, which is designed to self-extinguish within 5 meters when exposed to a flame. Additionally, it does not release toxic smoke or vapor, making it suitable for installation in ventilation ducts or air-return pressure systems used in HVAC equipment.
Post time: Feb-20-2025